Understanding the ncd national program: India’s Fight Against Non-Communicable Diseases
Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs): A Growing Global Challenge
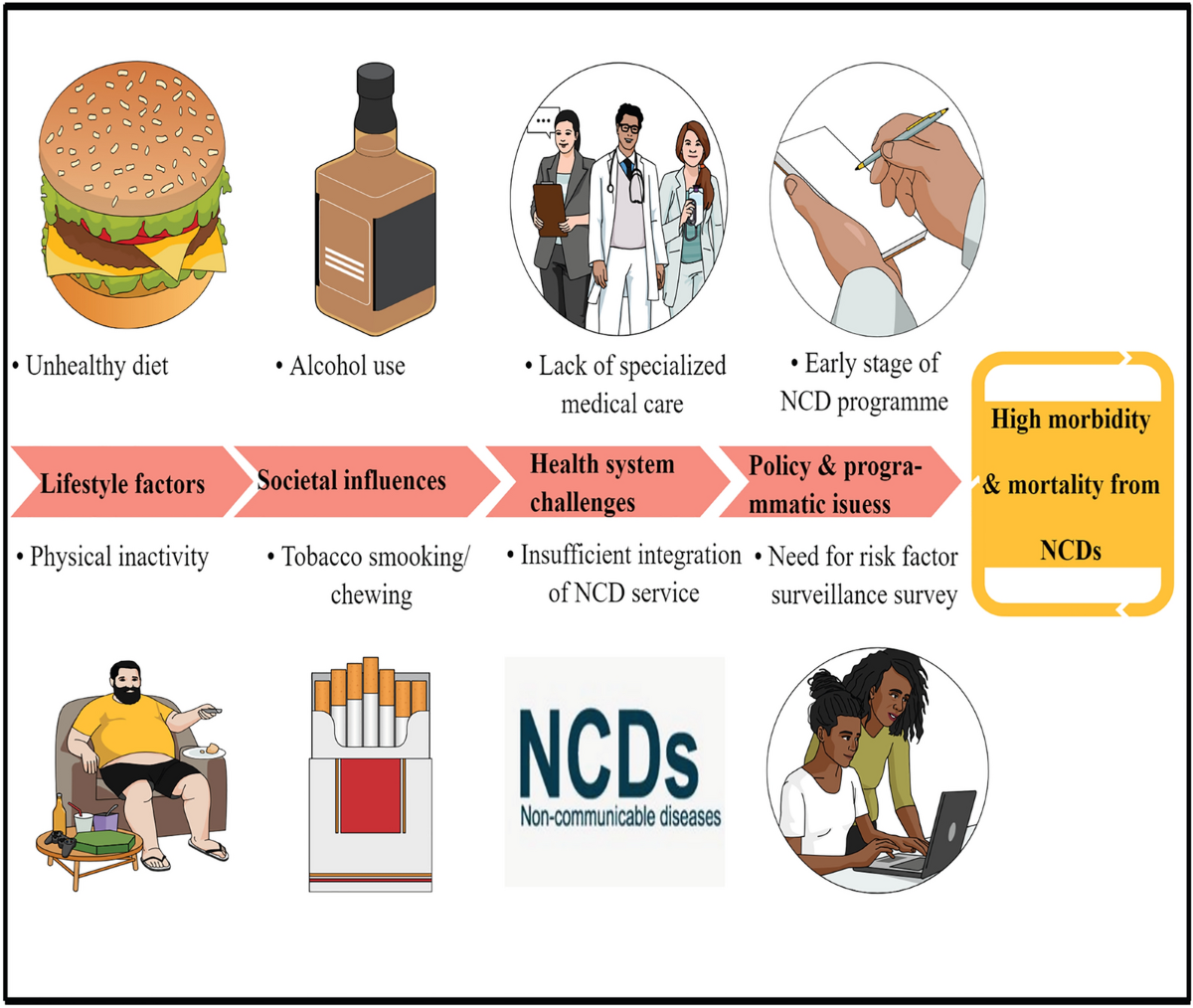
India is experiencing a health transition where lifestyle-related diseases are becoming more common than infectious ones. Diabetes, hypertension, cancer, and cardiovascular conditions are increasing rapidly, creating a heavy burden on families and the healthcare system. To address this challenge, the Government of India launched the ncd national program under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. This initiative focuses on prevention, early diagnosis, treatment, and awareness about non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
What is the ncd national program?
The ncd national program (National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke – NPCDCS) was started in 2010. Its main goal is to strengthen health systems to deal with the growing threat of lifestyle-related diseases.
The program includes:
- Screening of high-risk individuals.
- Early diagnosis of major NCDs.
- Referral and follow-up through health centers.
- Training of healthcare workers.
- Health awareness campaigns in rural and urban areas.
Key Objectives of the Program
- Prevention through Lifestyle Changes
- Encourage healthy diets, physical activity, and avoidance of tobacco and alcohol.
- Early Detection and Diagnosis
- Conduct regular screening camps at Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs).
- Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure
- Establish NCDs clinics at district hospitals and Community Health Centres.
- Capacity Building
- Train doctors, nurses, and frontline workers for better NCDs management.
- Promoting Awareness
- Run large-scale awareness campaigns in schools, workplaces, and communities.

Structure of the Program
- National Level
- Policies framed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- State and District Level
- State health departments implement the program.
- Dedicated NCDs cells at district hospitals manage local operations.
- Community Level
- ASHA workers and frontline healthcare staff screen people for early signs of NCDs.
Achievements So Far
- Over 10 crore screenings conducted at Health and Wellness Centres.
- Establishment of district-level NCD clinics across India.
- Integration of ABHA ID (Ayushman Bharat Health Account) for digital records.
- Awareness drives against tobacco and junk food in schools and workplaces.
Challenges in Implementation
- Lack of awareness among rural populations.
- Shortage of trained healthcare staff in remote areas.
- Lifestyle habits such as tobacco and alcohol use.
- Limited digital access in underdeveloped regions.
Future Roadmap
The government plans to expand the ncd national program by:
- Strengthening telemedicine for rural patients.
- Using Artificial Intelligence for predictive diagnosis.
- Expanding mobile screening vans in villages.
- Increasing collaboration with NGOs and private sector hospitals.
Why This Program is Important
- For Patients: Offers free or affordable diagnosis and treatment.
- For Families: Reduces long-term medical expenses.
- For the Nation: Helps in reducing premature deaths and increasing productivity.
Conclusion
The ncd national program is a vital step toward addressing the rising burden of lifestyle-related diseases in India. By focusing on prevention, early detection, and integrated digital healthcare, the program ensures healthier communities and reduces the impact of NCDs on the nation’s economy. With continued awareness and stronger implementation, this initiative has the potential to transform India’s healthcare system.