ncd portal Exploring the Role of the India’s Fight Against Lifestyle Diseases
Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs): A Growing Global Challenge
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like diabetes, cancer, hypertension, and heart disease are the biggest health threats facing India today. They cause over 60% of deaths in the country and put immense pressure on families and the healthcare system. To address this, the Government of India developed the ncd portal, a centralized digital platform that supports screening, diagnosis, and monitoring of NCDs across states.
This blog explains how the portal works, its key features, benefits, and how it is shaping the future of healthcare delivery.
What is the ncd portal?
The ncd portal is an online platform launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) under the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS).
Its main objective is to:
- Digitize patient records.
- Facilitate large-scale screenings.
- Provide real-time data for better policy decisions.
- Ensure follow-up and continuity of care.
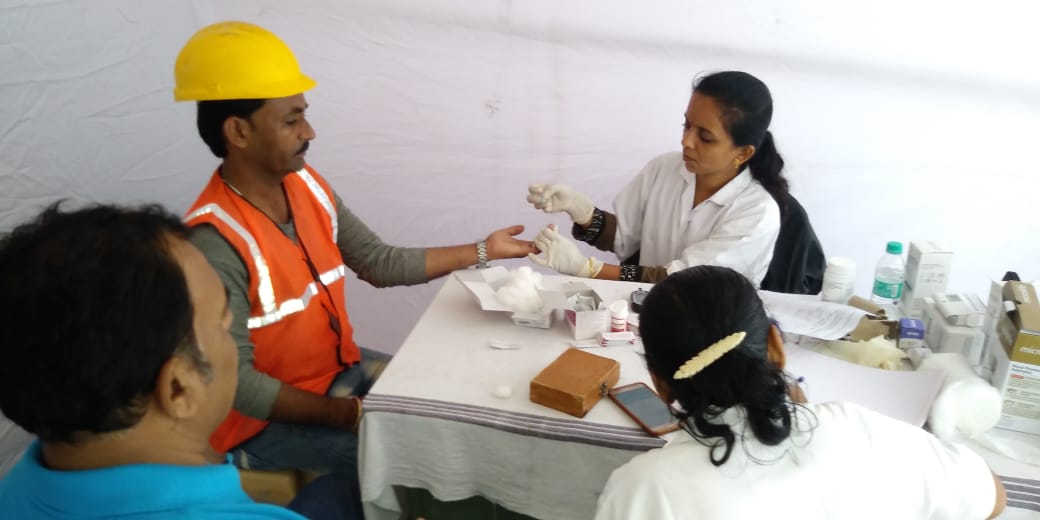

Key Features of the ncd portal
- Patient Registration
- Health workers can register patients at Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs).
- Information such as age, gender, medical history, and screening results is recorded.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
- Each patient has a digital record accessible across facilities.
- Reduces duplication of tests and improves treatment efficiency.
- Follow-Up Tracking
- The system sends reminders for regular check-ups.
- Ensures patients do not drop out of treatment programs.
- Reports and Analytics
- Generates reports at block, district, state, and national levels.
- Helps identify high-prevalence areas for targeted interventions.
- ABHA ID Integration
- Patients can link their health data with Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA ID).
Benefits of the ncd portal
- For Patients
- Ensures continuity of care across multiple hospitals.
- Saves money by avoiding repeated tests.
- Improves follow-up care.
- For Healthcare Workers
- Reduces paperwork with digital data entry.
- Provides real-time dashboards for managing patient lists.
- Improves coordination among different levels of the health system.
- For Policymakers
- Provides accurate, real-time statistics on NCDs.
- Supports evidence-based planning.
- Enables efficient use of healthcare resources.
Real-World Impact in ncd portal
- In Kerala, the portal has helped track hypertension cases in rural communities.
- In Telangana, it has supported large-scale screening programs for diabetes.
- Nationally, the system has created a more reliable dataset for planning health campaigns.
Why the Portal Matters
- Accountability and benchmarking: Countries can see where they stand relative to WHO goals and peer nations. This helps in assessing gaps.
- Evidence for policy: The data supports designing policies (for example, setting national NCD targets, creating guidelines, or planning prevention programs).
- Tracking progress: By looking at trends over time, one can see whether risk factors are increasing or decreasing, or whether policies are being implemented.
- Support to research and public health planning: Researchers, health systems, NGOs can use the data to target interventions more effectively.
Challenges and Limitations
While the NCD Data Portal is a powerful tool, there are several challenges:
- Data availability: Not all countries report every indicator; some have gaps in survey data, especially measured (vs self-reported) risk factor data. ncdportal.org+1
- Quality and consistency: Differences in how data is collected (survey design, clinical measurement, definitions) can make comparisons difficult.
- Implementation vs plan: Having policies or plans is one thing; actual implementation, funding, and real‐world enforcement are often inconsistent.
- Timeliness: Survey data and reports can have delays, meaning some statistics may lag behind current realities.
Looking Forward: Recommendations
To maximize the usefulness of the portal and strengthen the global response to NCDs:
- Increase investments in national data collection systems, ensuring surveys include measured biomarkers and behavioural risk factors.
- Standardize survey tools and data definitions to improve comparability.
- Strengthen implementation capacity: ensuring that policies, guidelines are not only developed but resourced and enforced.
- Promote more frequent and transparent reporting, ideally moving from five-year cycles to more frequent updates where possible.
- Encourage multisectoral collaboration (health, education, finance, agriculture, urban planning) since many NCD risk factors lie outside the health sector.
Challenges Faced by the Portal
- Internet issues in remote areas.
- Limited digital literacy among some healthcare staff.
- Awareness gaps among patients.
- Data privacy concerns that require strong security systems.
Future of the ncd portal
The government aims to strengthen the portal by:
- Adding mobile app access for easier usage.
- Integrating artificial intelligence to predict high-risk cases.
- Expanding coverage to more chronic diseases.
- Strengthening multilingual support for better inclusivity.
Conclusion
The ncd portal is a powerful tool in India’s fight against lifestyle diseases. By digitizing patient records and providing real-time data, it improves care for individuals while supporting policymakers with actionable insights. As technology and infrastructure improve, this platform will continue to play a vital role in reducing the burden of NCDs.